Follow us on LinkedIn
Education Savings Accounts, or ESAs, are a relatively a type of savings account that allows parents to save money for their child’s education. These accounts have become increasingly popular in recent years as more and more parents seek to find ways to pay for their children’s college educations. In this blog post, we will discuss the basics of Education Savings Accounts: what they are, how they work, and who is eligible to open one. We will also answer some common questions about ESAs, such as eligibility requirements and tax implications. So if you’re thinking about opening an ESA for your child’s education, be sure to read this post.
What is an Education Savings Account?
An ESA is an individual savings account specifically designed to save money for postsecondary education expenses. ESAs are similar to other types of saving accounts, but they come with certain tax advantages and restrictions that make them ideal for educational purposes.
How Does an Education Savings Account Work?
When you open an ESA, you can make contributions to the account with after-tax money. These contributions are not immediately taxable, and your investments grow tax-free. When it comes time for your child to use the money, any funds withdrawn from the account are also tax-free provided they are used to pay for qualified postsecondary education expenses such as tuition, books, fees, and supplies.
Who is Eligible to Open an Education Savings Account?
Generally, anyone can open an ESA. However, there are certain eligibility requirements that must be met in order to qualify for the tax advantages associated with ESAs. Depending on your state of residence, you may need to meet a certain income level or other criteria in order to open an ESA.
What are the Tax Implications of Education Savings Accounts?
As mentioned above, contributions to ESAs are not immediately taxable, and your investments grow tax-free. Withdrawals from the account will also generally be tax-free as long as you use them for qualified education expenses such as tuition, books, and supplies. However, there are certain restrictions on how much you can contribute each year as well as penalties for non-qualified withdrawals. Be sure to check with an accountant or financial advisor before opening an ESA in order to determine whether it is the right choice for you and your family.
What are the benefits of Education Savings Accounts?
There are many benefits to ESAs, including tax advantages and the ability to save for your child’s future. By investing in an ESA, you can ensure that your child is prepared for college without incurring debt or having to worry about paying for expenses out of pocket. Additionally, since these accounts come with certain restrictions, you can help your child make responsible financial decisions as they prepare for their future.
What are the drawbacks of Education Savings Accounts?
Though ESAs offer many advantages, there are some drawbacks as well. For example, contributions to an ESA are limited and you will have to pay taxes if the funds are withdrawn for non-qualified expenses. Additionally, ESAs may not be the best choice for everyone. Depending on your financial situation and the type of education you want for your child, other savings accounts may be more beneficial.
FAQs
What are the eligibility criteria for opening an Education Savings Account?
The eligibility requirements vary by state, but generally, you must meet certain income requirements and other criteria in order to qualify for the tax advantages associated with ESAs. Be sure to check with your state’s Department of Education or a financial advisor for more information.
Are contributions to Education Savings Accounts tax-deductible?
No, contributions to ESAs are not tax-deductible. However, your investments are allowed to grow tax-free, and withdrawals from the account will generally be tax-free as long as you use them for qualified education expenses such as tuition, books, and supplies.
Are there any restrictions on how much I can contribute to an Education Savings Account?
Yes, there are certain restrictions on how much you can contribute each year. Be sure to check with an accountant or financial advisor before opening an ESA in order to determine the maximum contribution for your situation.
How can I ensure my Education Savings Account funds are used for qualified expenses?
The best way to ensure that your ESA funds are used for qualified expenses is to discuss the details with your financial advisor and create a plan for responsible spending. Additionally, you should review IRS guidelines to make sure that any purchases are eligible for tax-free treatment.
Are there fees and commissions associated with Education Savings Accounts?
Yes, there may be fees or commissions associated with ESAs that you should consider when making your decision. Be sure to consult with a financial advisor or review the ESA documents in order to understand any associated costs.
Do I have to use my Education Savings Account funds for college expenses?
No, you do not have to use your ESA funds exclusively for college expenses. The funds can be used for any qualified education expenses such as tuition, books, and supplies. Additionally, the funds can be used to pay for private school tuition or K-12 expenses.
Are there penalties if I withdraw funds from my Education Savings Account?
Yes, there are strict rules and regulations with ESAs, and if you withdraw funds for non-qualified expenses you could be subject to penalties. Be sure to check with your state’s Department of Education or a financial advisor before making any withdrawals.
What should I consider when deciding between an Education Savings Account and another type of savings account?
When deciding between an ESA and another type of savings account, you should consider your financial goals and the types of education expenses that you would like to cover. Additionally, you should compare the potential tax advantages and other features of both accounts to determine which one is best for your situation.
What happens to the Education Savings Account funds if my child does not go to college?
If your child does not attend college or use their ESA funds for qualified expenses, you will be subject to taxes and penalties on any distributions from the account. However, many states allow you to transfer the funds from an ESA to another family member or use the money for other educational expenses such as graduate school or private school tuition. Be sure to check with your state’s Department of Education or a financial advisor for more information on the specifics of your situation.
What are the age restrictions for opening an Education Savings Account?
Generally, you can open an ESA at any age, but you must be the legal guardian of the beneficiary, which is typically a child. Additionally, your state may have specific rules regarding the age of the beneficiary. Be sure to check with your state’s Department of Education or a financial advisor for more information.
Are there any investment options available with Education Savings Accounts?
Yes, many ESAs offer a variety of investment options to help you grow your savings. Be sure to review the details of your ESA plan in order to understand your available options. Additionally, you should consult with a financial advisor to determine an appropriate strategy for achieving your goals.
The bottom line
Overall, Education Savings Accounts are a great way to save for your child’s education and ensure that they have the resources needed to succeed. By opening an Education Savings Account (ESA), you can help your child prepare for their future and enjoy certain tax advantages in the process. Be sure to check with a financial advisor and familiarize yourself with the restrictions and guidelines before opening an ESA in order to make sure it is the right choice for your family.
Further questions
What's your question? Ask it in the discussion forum
Have an answer to the questions below? Post it here or in the forum
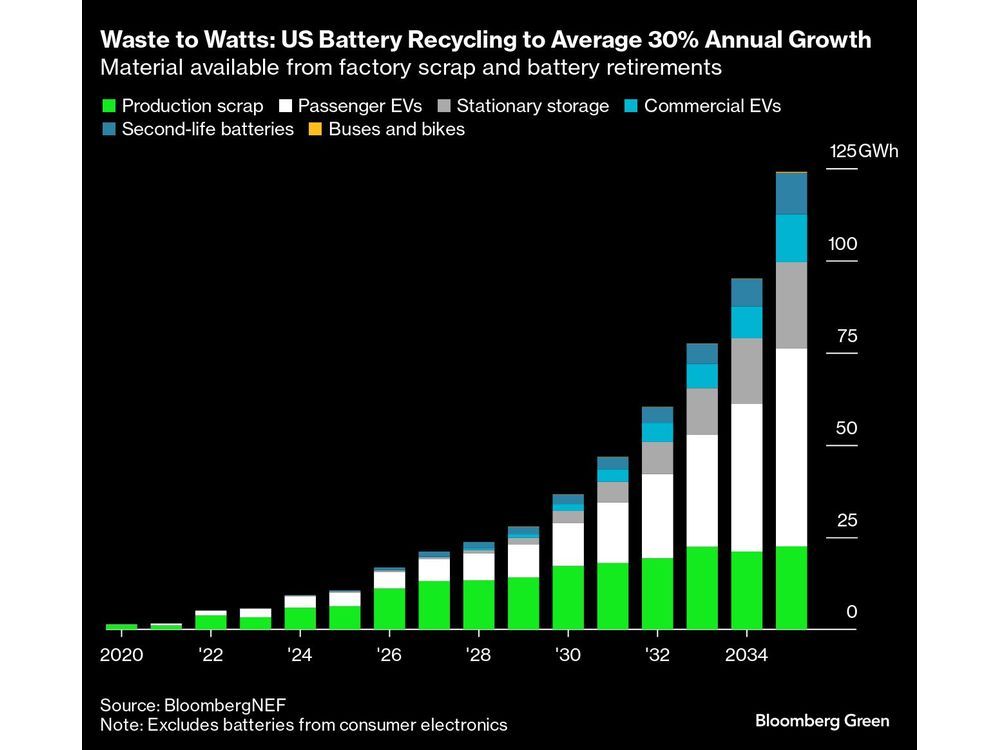
A first look inside the high-tech recycling machine that’s gobbling up the equivalent of 250,000 dead EV batteries a year.

“I don’t like it when people compare watches with stocks. This sends the wrong message and is dangerous,” Rolex’s Jean-Frédéric Dufour said.


