Follow us on LinkedIn
Monetary and fiscal policy are tools that can influence economic activity, whether it is to encourage or curb growth. Both fiscal and monetary policy can help stabilize the economy in times of a crisis or stimulate growth when the economy becomes stagnant. However, there are some differences between them.
What is Fiscal Policy?
Fiscal policies aim to target the total level of spending, the total composition of spending, or both in an economy. Fiscal policy refers to the use of government spending and tax policies to influence economic conditions, especially macroeconomic. These include conditions such as demand for goods and services, employment, inflation, and economic growth.
With fiscal policies, governments aim to influence a healthy economy. Similarly, governments don’t target anything specific with these policies, unlike monetary policies. They use two tools at their disposal, taxes, and spending. There are various ways that governments may use fiscal policies in practice.
For example, governments may increase their spending or decrease taxes to elevate businesses. However, they may also do the opposite to slow business activity in a country. With these policies, governments seek to stimulate the economy. Influencing economic outcomes through fiscal policies is one of the primary principles of Keynesian economics.
What is Monetary Policy?
Monetary policy does not come directly from governments but rather from central banks. A country’s central bank uses these policies to stimulate the economy or check its growth. With monetary policies, the aim is to stimulate demand. Monetary policy refers to the actions that a country’s central bank may take to control the money supply and achieve macroeconomic goals to promote sustainable economic growth.
The monetary policy includes drafting, announcing, and implementing the plan of actions that the central bank takes. It may also consist of other authorities within a country that controls the quantity of money or money supply. The tools that these authorities use to develop a monetary policy are money supply and interest rates. Similarly, the target with these policies is to meet macroeconomic objectives.
For example, a country’s central bank may decrease the money supply to control inflation and growth. In the US, the Federal Reserve uses monetary policies to regulate the economy, such as open market operations, changing reserve requirements for banks, and setting the discount rate. As mentioned, these are tools that influence either the money supply or interest rates.
What are the differences between Fiscal Policy and Monetary Policy?
Both fiscal and monetary policies have some differences. These are as below.
Source
Fiscal policies come from the government. Monetary policies, on the other hand, come from the central bank and other similar authorities.
Tools
Fiscal policies use spending and tax rates to affect economic factors. Monetary policies rely on money supply and interest rates to influence macroeconomic factors.
Effect
Since fiscal policies impact tax and government spending, it creates a budget deficit effect. On the other hand, monetary policies affect the cost of borrowing or mortgages.
Politics
Fiscal policies come from governments. Therefore, they have a strong political dimension to the changes. Monetary policies are independent of any politics.
Conclusion
Fiscal and monetary policies are tools that can affect economic activity. Fiscal policies come from governments and target the total level of spending and taxes. They influence economic conditions. Monetary policies come from central banks and similar authorities. These target macroeconomic goals. Both of these are different in various regards, as mentioned above.
Further questions
What's your question? Ask it in the discussion forum
Have an answer to the questions below? Post it here or in the forum
Meta rolled back January 6-era restrictions on former President Donald Trump's social media accounts ahead of the Republican National Convention.



June saw 75 filings, up from 62 in May and above the pandemic-era peak of 74 in July 2020, according to S&P Global Market Intelligence.
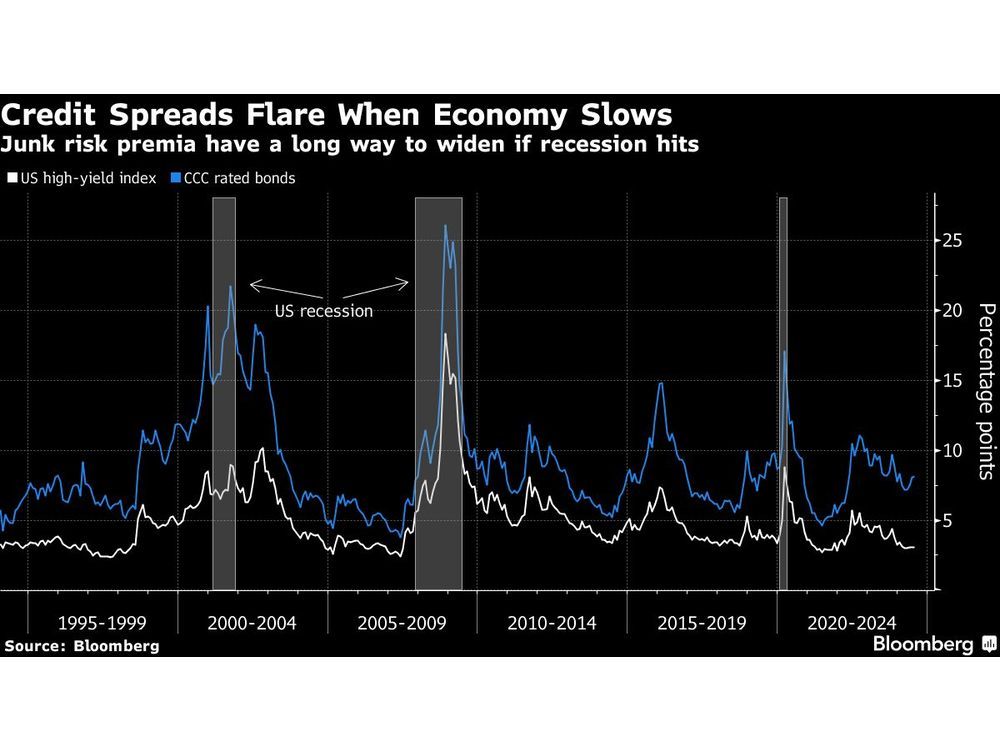
Credit markets are breathing a sigh of relief after inflation data showed price pressures are cooling broadly, but a weakening economy poses fresh risks to corporate debt.