Debt instruments are an important part of the capital market. In this post, we are going to provide an example of pricing a fixed-rate bond.
A fixed rate bond is a long term debt paper that carries a predetermined interest rate. The interest rate is known as coupon rate and interest is payable at specified dates before bond maturity. Due to the fixed coupon, the market value of a fixed-rate bond is susceptible to fluctuations in interest rates, and therefore has a significant amount of interest rate risk. That being said, the fixed-rate bond, although a conservative investment, is highly susceptible to a loss in value due to inflation. The fixed-rate bond’s long maturity schedule and predetermined coupon rate offers an investor a solidified return, while leaving the individual exposed to a rise in the consumer price index and overall decrease in their purchasing power.
The coupon rate attached to the fixed-rate bond is payable at specified dates before the bond reaches maturity; the coupon rate and the fixed-payments are delivered periodically to the investor at a percentage rate of the bond’s face value. Due to a fixed-rate bond’s lengthy maturity date, these payments are typically small and as stated before are not tied into interest rates. Read more
We are going to price a hypothetical bond as at October 31, 2018. We first build a zero coupon curve. Picture below shows the market rates as at the valuation date.
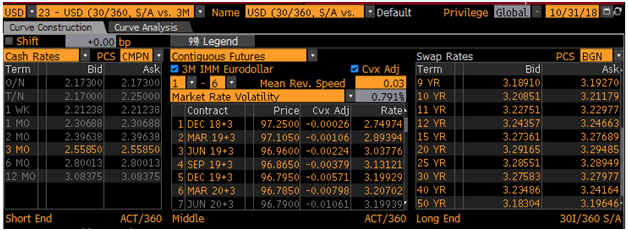
US swap curve as at Oct 31 2018
We utilize the deposit rates (leftmost column) to construct the zero curve up to 12-month maturity. We then use this zero curve to price the following hypothetical fixed rate bond:
Currency: USD
Maturity: 1 year
Payment frequency: semi-annual
Coupon rate: 3%
We use Python [1] to build a bond pricer. Picture below shows the result returned by the Python program. The price is $99.94 (per $100 notional).
![]()
In a follow-up post, we will discuss valuation of a callable bond.
References
[1] Balaraman and Ballabio, Quantlib Python Cookbook, Leanpub, 2017
To download the accompanying Excel workbook or Python program for this post:
1. Subscribe to the newsletter. If you're already a subscriber, go to the next step
2. Once subscribed, refer a friend
After completing these steps, you’ll gain access to the file for this post, along with files for a dozen other posts.
Further questions
What's your question? Ask it in the discussion forum
Have an answer to the questions below? Post it here or in the forum


nice
Useful !!