Follow us on LinkedIn
When auditors audit a client’s financial statement, they must reach some conclusions. Usually, these conclusions relate to whether the financial statements meet pre-identified suitable criteria. Once they do so, auditors must express their opinion. This opinion may either be unmodified or modified. Among modified audit opinions, auditors may also provide a qualified audit opinion.
What is Qualified Audit Opinion?
A qualified audit opinion is a type of modified opinion expressed by auditors. Auditors use the qualified opinion for two reasons. First, the client’s financial statements contain material misstatements. Second, auditors cannot obtain sufficient and appropriate audit evidence. However, the effects of these events must not be pervasive for auditors to express a qualified audit opinion.
The qualified audit report modifies the audit report. It is the reason why it is a part of the modified audit opinions category. Usually, the qualified audit report sends a negative signal to stakeholders. However, it is less serious compared to other modified opinions. Auditors usually use the qualified audit opinion for misstatements that have effects limited to specific financial statement items.
How does the Qualified Audit Opinion differ from other Modified Audit Opinions?
There are several differences between the qualified audit opinion and the other modified audit opinions. Further types of modified audit opinions include the adverse audit opinion and disclaimer of opinion. Overall, all three of these audit opinions fall under the modified audit opinion category. Therefore, all of these modify the audit report.
However, the qualified audit opinion still differs from the adverse opinion and disclaimer of opinion. The primary difference between these is that the qualified audit opinion is not for pervasive material misstatements. Pervasive is a term associated with how a misstatement affects the economic decisions made by users. If a material misstatement only exists in a specific financial statement item, it is not pervasive.
Another difference between the modified audit opinions is the wording on the audit report. The primary term that auditors use for the qualified audit report is “except for”. With this opinion, auditors specify the areas where material misstatements exist by excluding them from the rest of the financial statements. This way, auditors imply that these misstatements do not affect other areas of the financial statements.
Auditors also use the qualified audit opinion when they cannot obtain sufficient and appropriate audit evidence. Usually, auditors use the qualified opinion when supporting evidence for a specific item, material balance, or material transaction is unavailable. However, the effects of unavailable information are not pervasive.
What does the Qualified Audit Opinion express?
As it is a modified audit opinion, the qualified audit opinion sends a negative signal to stakeholders. However, it is not as serious as the adverse opinion or the disclaimer of opinion. Using the term “except for”, auditors exclude the rest of the financial statements from a modified opinion. They also specify the areas which caused them to qualify their opinion.
The qualified audit opinion, although negative, is not as serious. By excluding other items, auditors only point out a specific area where problems may exist. It is still up to users to alter or uphold their decisions related to the client’s business. Overall, the qualified opinion does not question the financial statements as a whole but parts of them.
Conclusion
Auditors provide opinions related to their findings during audit engagements. A qualified audit opinion is for material misstatements or audit evidence not being available. However, the effects of these issues must not be pervasive. Auditors use the term “except for” to exclude the rest of the financial statements from the qualified opinion.
Further questions
What's your question? Ask it in the discussion forum
Have an answer to the questions below? Post it here or in the forum
Meta rolled back January 6-era restrictions on former President Donald Trump's social media accounts ahead of the Republican National Convention.



June saw 75 filings, up from 62 in May and above the pandemic-era peak of 74 in July 2020, according to S&P Global Market Intelligence.
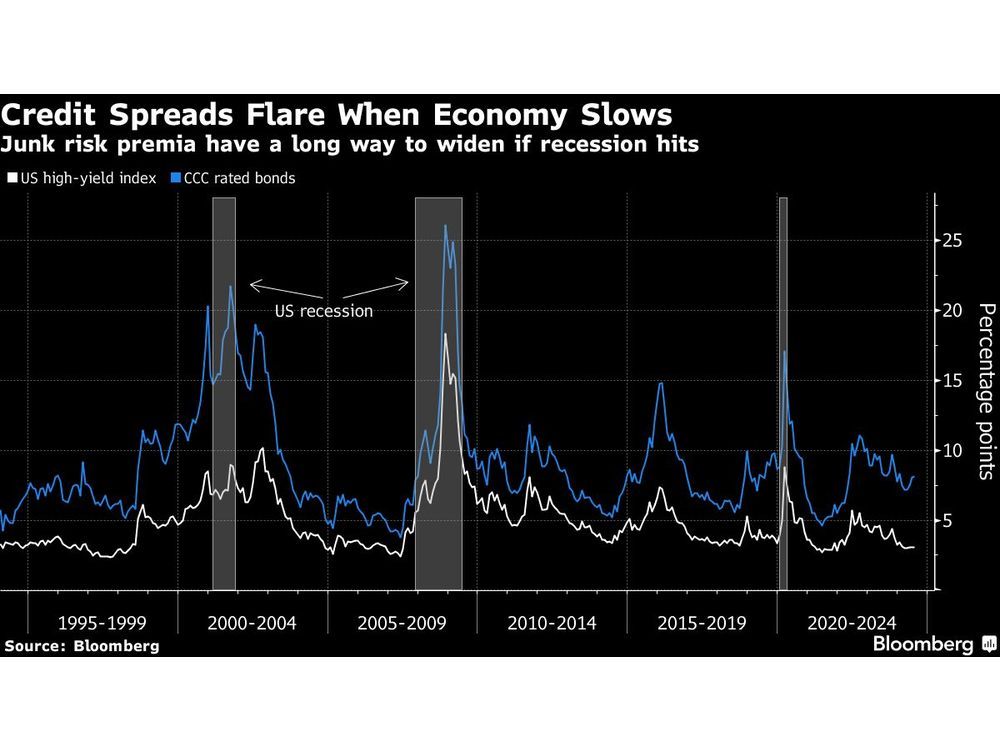
Credit markets are breathing a sigh of relief after inflation data showed price pressures are cooling broadly, but a weakening economy poses fresh risks to corporate debt.