R. Merton published a seminal paper [1] that laid the foundation for the development of structural credit risk models. In this post, we’re going to provide an example of how it can be used for managing credit risks.
Within the Merton model, equity of a firm is considered a call option on its asset, and it is expressed as follows,
![]()
where E denotes the equity of the firm,
V is the firm’s asset,
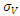 is the asset volatility,
is the asset volatility,
B is the notional amount of the debt,
r is the risk-free interest rate, and
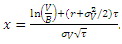
We note that both asset (V) and its volatility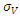 are not observable. However, the asset volatility can be related to equity and its volatility through the following equation,
are not observable. However, the asset volatility can be related to equity and its volatility through the following equation,
![]() where
where 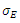 denotes the volatility of equity.
denotes the volatility of equity.
These 2 equations can be solved simultaneously in order to obtain V and its volatility 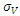 which are then used to determine the credit spread
which are then used to determine the credit spread
![]()
Having the credit spread, we will be able to calculate the probability of default (PD). Loss given default (LGD) can also be derived under Merton framework.
Graph below shows the term structures of credit spread under various scenarios for the leverage ratio (B/V).
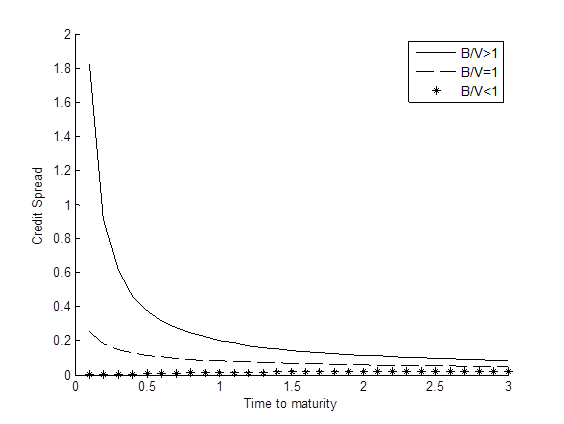
Term structure of credit spread
It’s worth mentioning that the Merton model usually underestimates credit spreads. This is due to several factors such as the volatility risk premium, firm’s idiosyncratic risks and the assumptions embedded in the Merton model. This phenomenon is called the credit spread puzzle. Research is being conducted actively in order to improve the model.
References
[1] Merton, R. C. 1974, On the Pricing of Corporate Debt: The Risk Structure of Interest Rates, Journal of Finance, Vol. 29, pp. 449–470.
Further questions
What's your question? Ask it in the discussion forum
Have an answer to the questions below? Post it here or in the forum



